What is Blazor?
Before we see the actual definition of Blazor, we must understand below
- For server-side development, we use programming languages like C#, Java, PHP etc. These are the server-side programming languages.
- For the client-side development we use JavaScript frameworks like Angular, React, Vue etc. There’s no doubt these JavaScript frameworks dominated client-side development up until recently.
- To stay in the business as a developer and remain competitive, it's inevitable we learn both a server-side programming language and a client-side programming language

- But the question is, why should we learn and use 2 different sets of programming languages and frameworks.
Can we use C# both for server-side and client-side development?
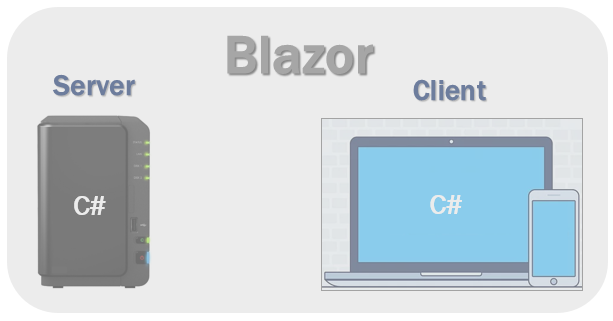
Blazor hosting models
Blazor offers 2 hosting models. Blazor WebAssembly and Blazor Server.
Blazor WebAssembly
This is also called the client-side hosting model and in this model, the application runs directly in the browser on WebAssembly. So, everything the application needs i.e the compiled application code itself, it's dependencies and the .NET runtime are downloaded to the browser. We use the Blazor WebAssembly App template, to create a Blazor application with the client-side hosting model. We will see this in action in our upcoming videos
Blazor server
Blazor Prerequisites
- C#
- HTML
- CSS
Blazor is gaining great traction and it is here to stay. If you are a .Net developer, it’s invaluable to have Blazor in your tool belt

Comments
Post a Comment